|
MiraMon offers a set of advanced tools in the fields of GIS, remote sensing and cartography that allow you to perform import/export operations, cropping, geometric corrections and reprojections, analysis, etc. The generic name of this set of tools is MiraMon Support Applications (MSA).
MSA are separate programs, independent of the MiraMon Windows graphical interface for viewing, querying, printing, etc., of raster and vector data, which are executed transparently with the same Windows interface. They can also be executed independently (from the command line) as explained below. Of the many reasons that have led to this design, the two most important are:
- The MiraMon functionalities that are not commonly used have been separated from the main core, allowing it to be much faster than if it included the applications in a single executable. This feature is especially important when running the program on a local network, over the Internet or on machines with few resources: keeping MiraMon small benefits users of less powerful machines, benefits multitasking processes on any computer and benefits other users of the network where MiraMon is on the server.
- Medium and advanced users, as well as professional practice, often need to repeat certain tasks a large number of times (format conversion for a large number of cartographic series files, geometric corrections of dozens of satellite spectral bands, etc.). Although the Windows interface is more user-friendly for first approaches or for occasional executions, when it is necessary to repeat tasks, this interface is annoying and not very operational. In these situations, the possibility of writing batch processing programs (Batch) and leaving relatively small applications working in the background (multitasking) is revealed as the best alternative.

The import format operations applications are located within the File menu. They are detailed below:
Menu |
Name of the application in the menu |
Name of the executable and access to its help
| Synopsis
|
File | Importing rasters |
TXT (ASCII)  IMG IMG |
ASCIIIMG
Importing ASCII raster files to MiraMon raster files |
Allows you to import raster files of various ASCII formats into MiraMon (IMG format): - ESRI ASCII raster format
- fixed record
- ASCII file with values separated by a delimiter formed by spaces, tabs or returns
- ASCII file with values structured in columns
|
E00 (Export ArcGIS/ArcInfo)  IMG IMG |
ArcInfMM
Conversion of vector and raster files between MiraMon and ArcGIS/ArcInfo (Export/interchange file) |
It allows you to go from a family of structured vector files from MiraMon to the export/"interchange file" (E00) format of ArcInfo (currently ArcGIS) and vice versa. The export format can also be read by ArcView.
|
BMP  IMG IMG |
Direct reading
from "File | Open raster" (BMP case) |
In the case of BMP, all files can be read directly in MiraMon through "File | Open raster" indicating the BMP extension. If you later want to convert the file to IMG, you must save it through "File | Save raster/WMS or WMTS as raster" choosing the "Entire raster" option.
|
JPEG  IMG/BMP IMG/BMP |
JPEGIMG
Conversion between JPEG and IMG or BMP raster files
| Transform between MiraMon IMG format or BMP format (without georeference), to JPEG format with MiraMon metadata, or to JPEG format without georeference.
|
JPEG2000  IMG, JPG, RGB IMG, JPG, RGB |
J2KIMG
Conversion between JPEG2000 and IMG or JPEG raster formats
| It allows you to obtain the information of the internal metadata of the JPEG2000 format, convert a JPEG2000 to JPEG format or to a raster (IMG, RGB or multiband, depending on the JPEG2000 file) or convert to JPEG2000 from a JPEG, raster (IMG, RGB, multiband or a REL file), ECW or SID format.
|
MrSID  IMG/JPEG IMG/JPEG |
SIDIMG
Importing the MrSID raster format to IMG or JPEG
| It allows you to obtain the information from the internal metadata of the MrSID format, import a MrSID to a JPEG format (gray or RGB, depending on the MrSID file) or extract between one and three IMG bands from a MrSID.
|
ECW  IMG/JPEG IMG/JPEG |
ECWIMG
Importing ECW raster to IMG or JPEG format
| It allows to obtain the information of the internal metadata of the ECW format, import an ECW to a JPEG format (gray or RGB, depending on the ECW file) or extract between one and three IMG bands of an ECW.
|
RST (Idrisi-32)  IMG IMG |
IdrMM
Import and export between Idrisi and MiraMon raster formats
| It transforms raster files between MiraMon and Idrisi-32.
|
HDF (ASTER, MODIS, NASAOcean[SeaWiFS, CTS, CZCS], PrOBA-CHRIS...)  IMG IMG |
HDFIMG
Import HDF raster format
| It allows to import HDF4 files to MiraMon raster format.
|
IMG (Idrisi)  IMG IMG |
Direct reading
from "File | Open raster" (in the case of Idrisi IMG) |
In the case of IMG (Idrisi), all files that are binary and uncompressed can be read directly in MiraMon through "File | Open raster".
|
LAN/GIS (Erdas 7.4)  IMG IMG |
ErdasIMG
Conversion between LAN or GIS (Erdas) files and IMG
| It allows putting several IMG files into one Erdas file of type LAN or GIS. On the other hand, it can also extract all the image bands contained on a LAN file and save them into different IMG files. GIS files only have one band and they are usually thematic files, not radiometric images.
|
CEOS (Landsat...)  IMG IMG |
CEOSIMG
Transforming rasters (satellite images, etc) from CEOS format to MiraMon IMG format |
It reads data from the ETM+ and TM sensors (Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus and Thematic Mapper) of the Landsat satellite in the CEOS format of the European Space Agency (ESA) as specified in the document: LANDSAT ETM+/TM - CEOS/ESA PRODUCTS FORMAT DEFINITION. V2.6. 13-June-2001. TM data from Landsat 5 has also been successfully read.
|
NDF (Landsat)  IMG IMG |
NDFIMG
Import from NDF raster format |
It transforms data from several satellite sensors (e.g., Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus, EMT+, Thematic Mapper, TM, Multispectral Scanner System, MSS, etc) of the Landsat series in the NDF format (NLAPS Data Format) of the United States Geological Survey (USGS)
|
JPEG2000 (Sentinel)  IMG IMG |
SentIMG
Importing images Sentinel-2 |
It imports data from the Sentinel-2 mission of the Sentinel satellite series, managed by the ESA to MiraMon format.
|
SPOT (TIFF+DIMAP)  IMG IMG |
SPOTIMG
Importing rasters in DIMAP (SPOT) format to MiraMon |
It reads data from SPOT series satellites (Satellite Pour l'Observation de la Terre) in DIMAP format (Digital Image Map).
|
TIFF, GeoTIFF  IMG IMG |
TIFIMG
TIFF-IMG format conversion |
It allows bidirectional transformation of TIFF and IMG files.
|
GRD (Surfer)  IMG IMG |
SurfMM
Import and export files in Surfer formats to MiraMon |
It allows the following transformations between Surfer formats and the formats of MiraMon: import grids, export rasters and export point files.
|
PGM/PPM (Meteosat, etc)  IMG IMG |
PGMIMG
Importing and exporting between PGM/PPM formats (Meteosat, etc) and MiraMon |
It allows to import and export the binary versions of the PGM and PPM formats.
|
CTL (GrADS)  IMG IMG |
GrADSIMG
Import GrADS raster format |
It allows to import raster files in format used by the software GrADS, frequently used in meteorology.
|
RF (Zebra)  IMG IMG |
ZebraIMG
Import Zebra (rf) format |
It allows the import of files from the Zebra format software, used principally for satellite and radar images in the meteorological field, to the MiraMon format.
|
RAW  IMG IMG |
RawIMG
Import and export between binary raster formats (BSQ, BIL, BIP) and MiraMon IMG |
It allows the conversion of binary files (usually from ENVI) and IMG files.
|
File | Import vectors and/or
databases |
DBF, Access, etc  PNT PNT |
BDPNT
Obtain PNT points from a database (local or remote) |
It obtains point type (X,Y) geographic locations from fields in a table in a (local or remote) database and creates a topologically structured points file in the MiraMon PNT format.
|
DXF  MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL), VEC MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL), VEC |
DXFVec
DXF files import |
It performs the conversion between DXF files (obtained with DXFOUT of AutoCAD, export of CorelDraw, etc.) and vectorial files, either topological structured (grouped in a MMM file) or not (VEC format).
|
DGN  MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL) MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL) |
DGN_MM
Import of Microstation files in DGN format to MiraMon formats |
It transforms data into DGN format, native to the Microstation computer-aided drawing program and widely used in the fields of engineering and architecture, in MiraMon. Currently, DGN files from version 7 and earlier are read.
|
SHP (Shapefile ArcGIS/ArcView)  PNT, ARC/NOD, POL PNT, ARC/NOD, POL |
SHPTop
Conversion between SHP vector files and MiraMon formats |
It converts an ArcGIS/ArcView Shapefile (SHP) into a MiraMon topological file (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL) and vice-versa.
|
E00 (Export ArcGIS/ArcInfo)  PNT, ARC/NOD, POL PNT, ARC/NOD, POL |
ArcInfMM
Conversion of vector and raster files between MiraMon and ArcGIS/ArcInfo (Export/interchange file) |
It performs the format conversion from a family of structured vector files of MiraMon to the Export/"interchange file" (E00) format of ArcInfo (currently ArcGIS), and vice versa. The export format can also be read by ArcView.
|
ArcSDE  PNT, ARC/NOD, POL PNT, ARC/NOD, POL |
SDEMM
Conversion from ArcSDE spatial databases to MiraMon formats |
It imports an ArcSDE layer, interface for accessing geodatabases designed by ESRI, to the MiraMon topological format (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL).
|
Oracle SDO (DSN)  PNT, ARC/NOD, POL PNT, ARC/NOD, POL |
SDOMM
Conversion from SDO spatial databases to MiraMon formats |
It imports a layer stored in a Spatial Oracle database to the MiraMon structured format (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL); during the transformation, it is also possible to generate explicit topological structure.
|
LAS/LAZ (lidar)  PNT PNT |
LASPNT
Import of lidar data in LAS or LAZ format |
It allows to consult or import lidar data from files in LAS or LAZ format (compressed variant from the aforementioned format) to the MiraMon structured vector format of points PNT.
|
VEC (Idrisi)  PNT, ARC/NOD, POL PNT, ARC/NOD, POL |
Direct reading
from "File | Import | Vectors and/or databases | VEC (Idrisi) ((case of Idrisi's VEC))
| All Idrisi VEC (ASCII) files can be read directly in MiraMon through the "File | Open unstructured vector" menu.
|
VEC (Idrisi)  VEC VEC |
CDF (NetCDF)  PNT PNT |
NetCDFMM
Import NetCDF vector format |
It allows certain NetCDF formats to be imported into MiraMon structured vector point files PNT.
|
GML (Geography Markup Language)  MMM MMM |
GMLMM
Importing and exporting between GML format and MiraMon format |
It allows importing a file from a GLM format to a MiraMon Map (MMM) that contains layers in structured vector format of MiraMon (PNT, ARC/NOD, and POL). It also allows exporting from a MiraMon Map or from a layer in MiraMon vector format to GLM.
|
GPS  PNT, ARC/NOD PNT, ARC/NOD |
GarminMM
Data interchange with a Garmin GPS |
It loads and downloads objects (points and lines) from the models of GPS of the GARMIN range to MiraMon through the computer's serial and USB ports.
|
GPX (GPS eXchange Format)  MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD) MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD) |
GPXMM
Import and export between GPX and MiraMon format |
It allows to convert a GPX format file (GPS eXchange Format) into MiraMon structured vector format (PNT, ARC/NOD) and viceversa.
|
KML, KMZ (Google Earth)  MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL) MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL) |
KMLMM
Conversion of KML files to MiraMon Maps |
It converts a GoogleEarth KML file into MiraMon Maps which contain layers in MiraMon structured format (PNT, ARC/NOD and POL).
|
GeoJSON  MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL) MMM (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL) |
JSONMM
Import and export between GeoJSON and MiraMon format |
It allows importing a file from GeoJSON format to MiraMon Map format (MMM) that contains layers in MiraMon structured vector format (PNT, ARC/NOD and POL). It also allows to export a MiraMon Map or a layer in vector format from MiraMon to GeoJSON.
|
CSV  DBF DBF |
DBFCSV
Conversion between DBF and CSV files |
It converts files from the DBF format (dBASE tables in classic DBF format or in extended DBF) to the CSV format (export of Excel tables) and vice-versa.
|

Applications for export formats are located within the File menu. They are detailed below:
Menu |
Name of the application in the menu |
Name of the executable and access to its help
| Synopsis
|
File | MiraMon maps export |
MMM  EMF/WMF (metafitxers) EMF/WMF (metafitxers) |
Export
from File | Print
+ press  | It allows exporting to a file of type EMF (Enhanced MetaFile), WMF (Windows MetaFile), BMP (BitMaP del Windows) or JPG (Joint Photographic Exports Group) instead of sending the job to the printer.
|
File | Raster export |
IMG  TXT (ASCII) TXT (ASCII) |
IMGASCII
Export to ASCII format from MiraMon raster |
It generates an ASCII text file from a MiraMon raster format file: img+i.rel in version 4 or img+doc in previous versions.
|
IMG  BMP BMP |
Direct reading
from "File | Save as BMP
| To save an IMG file or an RGB composition as a Windows bitmap, open it with MiraMon via "File | Open raster" or "File | Open RGB->24 bits" and execute "File | Save as BMP"
|
IMG/BMP  JPEG JPEG |
JPEGIMG
Conversion between JPEG and IMG or BMP raster formats |
It converts between the MiraMon IMG format or the BMP format (without georeferencing), to the JPEG format with MiraMon metadata, or the JPEG format (without georeferencing).
|
IMG, JPG, RGB, MrSID, ECW  JPEG2000 JPEG2000 |
J2KIMG
Conversion between JPEG2000 and IMG or JPEG raster formats |
It allows to obtain information from the internal metadata of the JPEG2000 format, convert a JPEG2000 to JPEG format or to a raster (IMG, RGB or multiband, depending on the JPEG2000 file) or convert to JPEG2000 from a JPEG, raster (IMG, RGB, multiband or a REL file), ECW or SID format.
|
IMG  RST (Idrisi-32) RST (Idrisi-32) |
IdrMM
Import and export between Idrisi and MiraMon raster formats |
It transforms raster files between MiraMon and Idrisi-32. The types of transformations that can be carried out are:
- Export of a band of any MiraMon IMG format to Idrisi-32 RST format.
- Import of Idrisi-32 in RST monoband format to MiraMon IMG.
- Export of MiraMon georeferenced JPEGs (J.rel) to a three-RGB band RST file of Idrisi-32.
|
IMG no bit, no long neither compressed  IMG (Idrisi) IMG (Idrisi) |
Direct reading
from "Export | IMG  IMG (Idrisi) (case IMG bit, long or compressed) IMG (Idrisi) (case IMG bit, long or compressed)
| All uncompressed and non-bit or long MiraMon IMG files are directly compatible with Idrisi.
|
IMG bit, long or compressed  IMG (Idrisi) IMG (Idrisi) |
IMGIMG
IMG files conversion and compression/uncompression |
It compress and uncompress raster files and for converting between IMG formats.
|
IMG  LAN/GIS (Erdas 7.4) LAN/GIS (Erdas 7.4) |
ErdasIMG
Conversion between LAN or GIS (Erdas) files and IMG |
It allows putting several IMG files into one Erdas file of type LAN or GIS. On the other hand, it can also extract all the image bands contained on a LAN file and save them into different IMG files. GIS files only have one band and they are usually thematic files, not radiometric images.
|
IMG  TIFF, GeoTIFF TIFF, GeoTIFF |
TIFIMG
TIFF-IMG format conversion |
It allows bidirectional transformation of TIFF and IMG files.
|
IMG  PGM/PPM (Meteosat, etc) PGM/PPM (Meteosat, etc) |
PGMIMG
Importing and exporting between PGM/PPM formats (Meteosat, etc) and MiraMon |
It allows to import and export the binary versions of the PGM and PPM formats.
|
IMG  GRD (Surfer) GRD (Surfer) |
SurfMM
Import and export files in Surfer formats to MiraMon |
It allows the following transformations between Surfer formats and the formats of MiraMon: import grids, export rasters and export point files.
|
IMG  RAW RAW |
RawIMG
Import and export between binary raster formats (BSQ, BIL, BIP) and MiraMon IMG |
It allows the conversion of binary files (usually from ENVI) and IMG files.
|
File | Vectors and tables export |
PNT  DBF (x,y,z) DBF (x,y,z) |
PNTBD
Export of PNT files to DBF tables with coordinates |
It exports PNT files to DBF tables with x,y,z coordinates for each point.
|
PNT, ARC, NOD, POL, VEC  DXF DXF |
VecDXF
Export MiraMon vector layers to DXF files |
It converts structured vector files of points, arcs, polygons, or nodes (PNT, ARC, POL, or NOD formats) and unstructured files of points, lines, or polygons (VEC format) to DXF format, which is importable by AutoCAD (see the DXFIN command in the AutoCAD manual) and other programs such as MicroStation, CorelDraw, or MS-Word. It also exports the 3D model if present in the source formats.
|
PNT, ARC/NOD, POL  SHP (Shapefile ArcGIS/ArcView) SHP (Shapefile ArcGIS/ArcView) |
SHPTop
Conversion between SHP vector files and MiraMon formats |
It converts an ArcGIS/ArcView Shapefile (SHP) into a MiraMon topological file (PNT, ARC/NOD, POL) and vice-versa.
|
PNT, ARC/NOD, POL  E00 (Export ArcGIS/ArcInfo) E00 (Export ArcGIS/ArcInfo) |
ArcInfMM
Conversion of vector and raster files between MiraMon and ArcGIS/ArcInfo (Export/interchange file) |
It performs the format conversion from a family of structured vector files of MiraMon to the Export/"interchange file" (E00) format of ArcInfo (currently ArcGIS), and vice versa. The export format can also be read by ArcView.
|
VEC  VEC (Idrisi) VEC (Idrisi) |
Direct reading
from "File | Export VEC  VEC (Idrisi)" (case of unstructured vectors VEC) VEC (Idrisi)" (case of unstructured vectors VEC)
| In the case of unstructured MiraMon vectors (VEC), all files are directly compatible with Idrisi (VEC) files and, therefore, export is not necessary, except for those with string and integer type attributes with attributes outside the range [-32768,32767]; in these latter cases, it is necessary to reclassify the attributes to one of the types supported by Idrisi (short integer or real).
|
PNT, ARC/NOD, POL  GML (Geography Markup Language) GML (Geography Markup Language) |
GMLMM
Importing and exporting between GML format and MiraMon format |
It allows importing a file from a GLM format to a MiraMon Map (MMM) that contains layers in structured vector format of MiraMon (PNT, ARC/NOD, and POL). It also allows exporting from a MiraMon Map or from a layer in MiraMon vector format to GLM.
|
PNT, ARC/NOD  GPX (GPS eXchange Format) GPX (GPS eXchange Format) |
GPXMM
Import and export between GPX and MiraMon format |
It allows to convert a GPX format file (GPS eXchange Format) into MiraMon structured vector format (PNT, ARC/NOD) and viceversa.
|
MMM, PNT, ARC, POL  KML, KMZ (Google Earth) KML, KMZ (Google Earth) |
KMLMM
Conversion of KML files to MiraMon Maps |
It converts a GoogleEarth KML file into MiraMon Maps which contain layers in MiraMon structured format (PNT, ARC/NOD and POL).
|
MMM, PNT, ARC, POL  GeoJSON GeoJSON |
JSONMM
Import and export between GeoJSON and MiraMon format |
It allows importing a file from GeoJSON format to MiraMon Map format (MMM) that contains layers in MiraMon structured vector format (PNT, ARC/NOD and POL). It also allows to export a MiraMon Map or a layer in vector format from MiraMon to GeoJSON.
|
VEC  DAT (Surfer) DAT (Surfer) |
SurfMM
Import and export files in Surfer formats to MiraMon |
It allows the following transformations between Surfer formats and the formats of MiraMon: import grids, export rasters and export point files.
|
DBF  CSV CSV |
DBFCSV
Conversion between DBF and CSV files |
It converts files from the DBF format (dBASE tables in classic DBF format or in extended DBF) to the CSV format (export of Excel tables) and vice-versa.
|

The applications of topological structuring operations are found within the Edit menu. They are detailed below:
Menu |
Name of the application in the menu |
Name of the executable and access to its help
| Synopsis
|
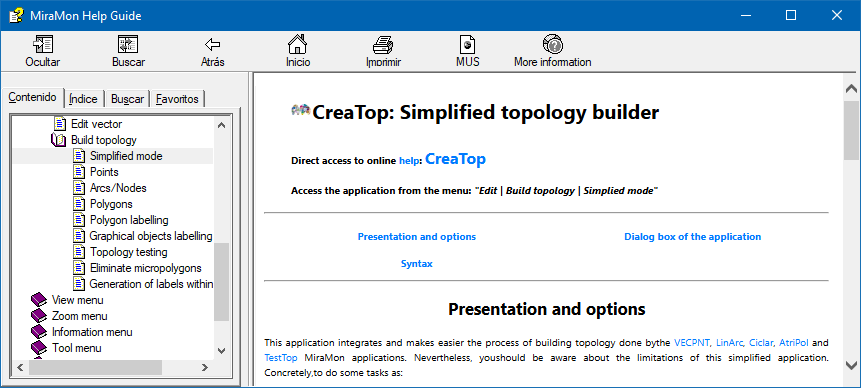
Edition | Build topology |
Simplified mode |
CreaTop
Simplified topology builder |
It allows you to quickly and easily create vector bases of points, arcs/nodes and polygons with topological structure. It allows you to select the tolerance threshold.
|
| Points |
VECPNT
Transformation between VEC and PNT (with and without topology) |
It allows you to transform point files in VEC (ASCII) format to point files in PNT format (binary and structured), and vice versa. It can also simplify a PNT file, grouping the points that are within a certain defined distance (tolerance) generating multiple records.
|
| Arcs/Nodes |
LinArc
Line topology building and conversion between ARC/NOD and VEC files |
It performs the conversion between VEC files containing lines and Top-MM structured vector files (ARC and NOD).
|
| Polygons |
Ciclar
Creating polygons with topology |
It allows building all the topological polygons present in the arc file. In addition, in the selection, arcs that would have the same polygon on both sides (halters) can be automatically removed.
|
| Polygon labelling |
AtriPol
Polygon labeling |
It adds attributes (labels) to the polygons generated with the Ciclar application. Attributes are added to the P.DBF file as new fields of the database.
|
| Graphical objects labelling |
AtriTop
Transfer of attributes between vector entities |
It transfers attributes from one graphical layer to another based on a geometrical relation between both of them. Therefore, attributes can be transferred from a point layer to a polygon layer, or vice versa, that is, attributes can be transferred to the points from the polygon they are in. Another example is the transfer of attributes from an arcs layer to a polygon layer. In this case, the polygons can receive the attributes of the arcs that are completely contained within them or the arcs can receive the attributes of the polygons they are in.
|
| Test topology |
TestTop
Test for topologically structured files |
It carries out some consistency tests on topologically structured files.
|
| Erase micropolygons |
MicroPol
Erase polygons and micropolygons of a polygon or categorical raster layer |
It allows removing micropolygons from a polygon file or a categorical raster.
|
| Generation of labels within polygons |
Etiqueta
Generation of labels within polygons |
It allows to generate points which are labels of polygons from a POL file (topologically structured or not), or a VEC file VEC (which is always an explicit polygon file with explicit polygons). The new generated labels can, or can not, get the preexisting attributes of the polygons and are written in the same order as in the original polygons. The program allows if desired, or not, to place a label on polygon zero (the external polygon, or the universal polygon, that envelopes the rest of polygons).
|

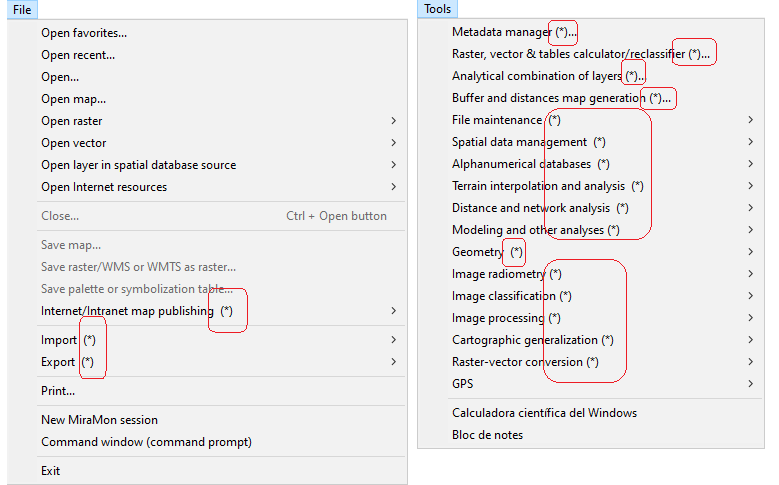
Applications for analysis operations, geometry, etc, with rasters and vectors are found in the Tools menu, grouped by topics (file maintenance, spatial organization, etc). They are detailed below:
Menu |
Name of the application in the menu |
Name of the executable and access to its help
| Synopsis
|
Tools | General tools |
Raster, vector & table calculator/reclassifier |
CalcImg
Layers and fields Calculator/Reclassifier: Mathematical and Logical Analysis |
It allows performing reclassifications and mathematical and logical operations, simultaneously, on layers of any type (rasters, structured vectors and unstructured vectors).
|
| Analytical combination of layers |
CombiCap
Analytical combination of raster and vector layers |
It analyses and/or performs a spatial combination of two raster layers, a raster layer and a vector layer or two vector layers.
|
| Buffers and distance maps generation |
BufDist
Influence areas (buffers) and distance maps generation |
It allows the creation of both continuous distance maps (raster result) and influence maps (buffers) at a specified distance from the target entities (raster and vector result).
|
Tools | File maintenance |
Compression and uncompression of MMZX/MMZ files |
MMZ
Compression and uncompression of MMZX/MMZ files (diffusion, preservation, etc; limited version) |
It compresses and uncompresses both MMZ files (compressed MiraMon files) and their standardized evolution, MMZX files.
|
| Create a new raster |
CreaRas
Create a new raster |
It creates a new raster from a pre-existing pattern file or with given characteristics that are entered manually.
|
| Conversion of IMG files among any of the MiraMon supported formats |
IMGIMG
Conversion of IMG files among any of the MiraMon supported formats |
It is used to compress/uncompress raster files and to perform format conversions (real->integer, etc).
|
| Generation of labels within polygons |
Etiqueta
Generation of labels within polygons |
It allows to generate points which are labels of polygons from a POL file (topologically structured or not), or a VEC file VEC (which is always an explicit polygon file with explicit polygons). The new generated labels can, or can not, get the preexisting attributes of the polygons and are written in the same order as in the original polygons. The program allows if desired, or not, to place a label on polygon zero (the external polygon, or the universal polygon, that envelopes the rest of polygons).
|
| Obtain PNT points from a DBF, Acces, etc database |
BDPNT
Obtain PNT points from a database (local or remote) |
It obtains point type (X,Y) geographic locations from fields in a table in a (local or remote) database and creates a topologically structured points file in the MiraMon PNT format.
|
| Emancipate polygons from arcs |
Emancipa
Extraction of the minimum base of arcs for a given polygon file |
It allows selecting a subset of arcs from the general arc database and generating a polygon file that is linked to this new arc database or obtaining independence from the original source file itself.
|
| Conversion of layers between MiraMon formats 1 and 4 |
ConvREL
Conversion of layers between MiraMon formats 1 and 4 |
Transforms the links between tables, metadata and symbols from older versions to the 4/5 version. It also permits the user to return to older versions of the program with more limited features.
|
| Conversion or marking ANSI/OEM/UTF-8 |
ANSIOEM
Character set conversion or marking in ANSI (Windows), OEM (DOS) or UTF-8 files |
Converts file in plain text or in DBF format between ANSI (Windows), OEM-850 (DOS) and/or UTF-8 character sets. This way, they can be visualized and edited correctly either with Windows (notepad) or MS-DOS editors (as EDIT).
In the case of ANSI-OEM-UTF8 marking, it allows marking the character set of files in DBF format as OEM-850 (DOS), ANSI, UTF-8, or other sets.
|
Tools | Spatial data management |
Layer clipping |
Retalla
Layer clipping |
It clips IMG, JPG, WMS, and structured and not structured vectors, whether by field or by mask.
|
| Mosaic and join layers |
Mosaic
Mosaic and join layers |
Generates a resulting layer from the union of the original layers from a set of layers that cover a specific area.
|
| Joining two or more vector files |
UnirVec
Joining two or more vector files |
It joins two or more MiraMon vector files into a single file without taking any topological consideration. .
|
| Erase micropolygons |
MicroPol
Erase polygons and micropolygons of a polygon or categorical raster layer |
It allows removing micropolygons from a polygon file or a categorical raster.
|
| Vector entities scalling and shifting |
EscalVec
Vector entities scalling and shifting |
This program performs a change of scale and/or a shift of vector files in non-structured VEC format. It also changes map coordinates to paper coordinates as a prior step for exporting some drawing packages.
|
| Vertices of lines or polygons to points |
VrtPunt
Creation of a points file from vertices of lines or polygons |
Creates a file containing points from extractions from all lines or polygons vertices taken from a file.
|
| Raster fitting to another raster |
AdapRas
Raster fitting to another raster (extent and cell size) |
It fits a raster file according to a geometric pattern of another raster file, even when the pattern raster has a wider bounding box than the raster to be adapted.
|
| Raster densifying and dedensifying |
DensRas
Raster densifying and dedensifying (resampling) |
It changes the cell side of a raster (densifies or dedensifies it, as appropriate), without exceeding the bounding box of the original raster, and allowing, if necessary, a change of the origin grid.
|
| Changing raster pixel side (multiples) |
CanviRes
Changing raster pixel side (exact multiples) |
It changes a raster pixel side without changing its origin.
|
Tools | Alphanumerical databases |
View and edit Databases Tables |
MiraDades
View and edit Databases Tables |
MiraDades is the databases table viewer and editor for MiraMon with which it is possible to edit database contents, restructure fields or records, sort, join and perform the basic table operations needed in a geographical information system.
|
| Database Tables management and maintenance |
GestBD
Database Tables management and maintenance |
Set of tools and procedures for editing, revising, updating, etc different elements (table structure, fields and records) of databases and tables.
|
| Selection of a subset of vector entities |
VecSelec
Selection of a subset of vector entities |
It allows to select a subset of graphic objects from a file of points, arcs, nodes, polygons or groups of polygons and save them to a file of points, arcs, nodes, polygons or groups of polygons respectively.
|
| Fields statistics |
EstdCamp
Statistics of a table field or database query |
It does statistical calculations on a table field. This can be any physical table or query such as the associated with a graphic layer from its corresponding REL file, and it can also be an individual DBF table or a table or SQL query via ODBC of a MDB, Oracle, etc, database.
|
| Statistics of records groups |
EstdGrup
Fields statistics by grouping records according to values present in other fields |
It determines how many and which different values it presents in a data base, organized in a relational way based on the identifiers of the graphic objects of the main table.
|
Tools | Terrain interpolation and analysis |
Generation of Thiessen polygons |
Thiessen
Generation of Thiessen polygons |
It generates, from a layer that contains a set of point-type vector entities, a layer of polygons that will contain the corresponding Thiessen polygons.
|
| Variogram representation and modeling |
Vargram
Variogram representation and modeling |
It allows representing and modeling the so-called semivariogram, the spatial pattern describing the correspondence between semivariance and distance.
|
| Interpolation from point data, lidar |
InterPNT
Interpolation from point data, lidar |
It generates a raster in which each cell value is obtained by interpolation between the values in a numerical field of the database of a points file, or the third coordinate in the case of 3D files (where Z can be topographic, but can also be another variable, such as temperature, concentration of a pollutant, etc).
|
| Interpolation from contour lines |
IsoMDE
Generate Digital Terrain Models from contour lines |
It allows digital terrain models (DTMs) to be generated from all sorts of isolines, and may use other additional information like lines showing valleys, hillcrests, etc.
|
| Generation of contour lines from DTM |
MDTIso
Generation of contour lines from DTM |
It allows generating contour lines (also known as contour lines or isopleths) from a digital terrain model (DTM) (for instance elevation, rainfall, evapotranspiration, pollution, etc).
|
| TIN models generation |
CreaTIN
TIN models generation from a point cloud |
It allows generating a triangulated irregular network (TIN) from a file of points.
|
| TIN rasterization |
TiraVec
Rasterize vector files |
It takes a vector point file, a line/arc file, a polygon or node file (whether structured or not) and rasterizes it using an existing or new raster.
|
| DTM densifying and dedensifying |
DensRas
Raster densifying and dedensifying (resampling) |
It changes the cell side of a raster (densifies or dedensifies it, as appropriate), without exceeding the bounding box of the original raster, and allowing, if necessary, a change of the origin grid.
|
| DTM error detection |
ErrorMDT
DTM error detection |
It searches for locations in a Digital Terrain Model (MDT) that contain candidate values to be considered errors.
|
| Obtain 3D vectors from DEM |
Vec3D
Obtain 3D vectors from DEM |
It incorporates the third dimension into unstructured vector files (VEC) or PNT or ARC files based on the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) of the same area.
|
| Generate topographic profiles |
Perfils
Generate topographic profiles |
It generates topographic profiles for a specific itinerary using a Digital Elevation Model (DEM).
|
| Compute slopes, aspects, etc |
Pendent
Terrain analysis: Slopes, Aspects, etc |
It calculates, based on a Digital Elevation Model, several Digital Models (slope: MDP, aspect: MDO, etc) which are derived from the elevations, in order to describe and to characterize the relief.
|
| Compute solar radiation |
InsolDia
Computation of the solar radiation in a single day or an instant |
It calculates the incident solar radiation (in units of energy, not power) at each point on the ground during a given day of the year. It also allows to make the calculation in a time interval throughout the day (not all day) and instantaneously at a specific moment of the day.
|
| Hillshading maps generation |
Ombrejat
Hillshading of raster and polygon layers |
It allows to obtain shadowed images (through light gradation) according to the relief and the position of the Sun.
|
| Visibility analysis |
Visible
Visibility analysis |
It determines, through the Digital Elevation Model (DEM), which pixels are visible and which are not, via a set of observers or viewpoints.
|
| Compute solar radiation |
Astres
Obtention of the Sun azimuth and elevation in a place, a date and hour on the Earth |
It computes, for a place in the Earth given in geographic coordinates, a day and a local solar hour or UTC, the azimuth and elevation of the Sun.
|
| Obtain Digital Illumination Model |
Illum
Calculation of illumination at each point of a Digital Elevation Model |
It calculates, from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), the illumination received by a point in the terrain when the Sun occupies a certain position in the celestial sphere.
|
| Obtain Digital Shadow Model |
Ombra
Calculation of the limit angles that cause projected shadows in a DEM |
It calculates, from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and a given solar azimuth, the Sun elevation angle from which each point in the terrain (raster cell) gets direct light from the Sun (the point is not under the shadow of another point in that azimuth direction).
|
| Regions from punctual occurrences |
RegioPNT
Creating regions from punctual occurrences |
It generates a polygon vectorial layer from the thematic and spatial grouping of points. Typically it is used in the determination of regions of activity, influences, attends, etc of a certain species or variable, habitually booleana (0 or 1), from information received in punctual locations.
|
| Generation of 3D perspectives |
Visio3D
Generation of 3D perspectives based on a raster and its DEM |
It allows to generate a 3D perspective from a digital elevation model of any image: thematic, orthophotography or any continuous model like the DEM.
|
Tools | Distances
and network analysis |
Buffers and distance maps generation |
BufDist
Influence areas (buffers) and distance maps generation |
It allows the creation of both continuous distance maps (raster result) and influence maps (buffers) at a specified distance from the target entities (raster and vector result).
|
| Least cost path analysis |
GenCost
Minimal cost analysis of motion over a friction model |
It creates a cost raster from a friction model (pass resistance) and a target entities raster that you wish to reach.
|
| Network analysis (routes) |
Rutes
Network analysis and identification of the optimal route |
It determines the optimum routes between a set of origin locations and a set of possible destination locations.
|
Tools | Modeling and other analysis |
Multivariant regression |
RegMult
Multivariant regression and residual interpolation |
It constructs a predictive model of a Y spatial variable according to other (xn) independent spatial variables.
|
| Logistic regression |
RegLog
Logistic regression |
It allows generating an explanatory and predictive model of a Y spatial dichotomous variable based on n quantitative Xn independent spatial variables.
|
| Rank of cell values in a raster |
OrdreRas
Rank of cell values in a raster |
It generates a raster image of indexes according to the order (ascending or descending) that corresponds to the original input raster values.
|
| Spatial autocorrelation analysis (Moran) |
AutoCor
Spatial autocorrelation analysis (Moran) |
It allows quantifying the degree of spatial autocorrelation of a variable in a raster file by calculating an indicator, in this case the Moran's I(i) index.
|
| Calculation of evapotranspiration |
EvapoTr
Calculation of evapotranspiration |
It calculates evapotranspiration. The only option available is the calculation of potential evapotranspiration with the formula of Thornthwaite 1948.
|
| Habitats analysis |
AnHabit
Habitats analysis |
It allows analyzing layers of habitats in a biogeographic region and determines the representation level (in percentage) of a selection of those habitats on a set of interest areas differentiated by a code (interest areas).
|
Tools | Geometry |
Geodetic calculator |
CalcGeo
Geodetic calculator |
It allows the conversion of the coordinates of a point in a given reference system to the coordinates in another reference system.
|
| Change of Geographic Reference System (projection, datum, etc) |
CanviPrj
Change of Geographic Reference System (projection, datum, etc) |
It allows to transform from one projection system to another and also, to change the reference system by setting the projection parameters, the datum, the ellipsoid, etc.
|
| Convert VEC to control points (COR) |
VECCOR
Transformation of VEC files of points to COR files used by CorrGeom |
It transforms VEC files of point to the working format of CorrGeom program.
|
| Elemental corrections (translation, rotation, etc) |
CorrGeom
Geometric correction of raster and vector files |
It allows applying different correction methods depending on the characteristics of the layer to be georeferenced:
- Polynomial corrections of raster and vector
- Generation of spatial orthoimages
- Orthophoto generation
- Geometric transformations (affix and perspective) of raster and vector
|
| Polynomial corrections (rasters and vectors) |
| Satellite orthoimage generation |
| Orthophoto generation |
| Convert Degrees/Hours, Min, Seg to Graus/Rad |
gms_g
Conversion between angle/hour units |
It allows to convert angular measurements:
- from sexagesimal degrees (degrees, minutes, and seconds) to decimal degrees (degrees and decimal fractions of a degree) and vice versa
- from sexagesimal or decimal degrees to radians and vice versa
|
Tools | Image radiometry |
Compute solar radiation |
Astres
Obtention of the Sun azimuth and elevation in a place, a date and hour on the Earth |
It computes, for a place in the Earth given in geographic coordinates, a day and a local solar hour or UTC, the azimuth and elevation of the Sun.
|
| Obtain Digital Illumination Model |
Illum
Calculation of illumination at each point of a Digital Elevation Model |
It calculates, from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), the illumination received by a point in the terrain when the Sun occupies a certain position in the celestial sphere.
|
| Obtain Digital Shadow Model |
Ombra
Calculation of the limit angles that cause projected shadows in a DEM |
It calculates, from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and a given solar azimuth, the Sun elevation angle from which each point in the terrain (raster cell) gets direct light from the Sun (the point is not under the shadow of another point in that azimuth direction).
|
| Radiometric correction |
CorRad
Radiometric correction of Remote Sensing images |
It allows the radiometric correction of remote sensing images captured in the visible and non-thermal infrared spectral regions.
|
| Emissivity computing |
Emissiv
Emissivity computing |
It allows calculating emissivity based on a band in the red spectral region and a band in the infrared spectral region.
|
| Earth Surface Temperature computation |
TST
Earth Surface Temperature computation |
It is used to calculate the temperature of Earth surface according to emissivity data, steam, and a thermal band. Air temperature data could also be added.
|
| Convert Degrees/Hours, Min, Seg to Graus/Rad |
gms_g
Conversion between angle/hour units |
It allows to convert angular measurements:
- from sexagesimal degrees (degrees, minutes, and seconds) to decimal degrees (degrees and decimal fractions of a degree) and vice versa
- from sexagesimal or decimal degrees to radians and vice versa
|
Tools | Image classification |
Compute spectral signatures and spectral statistics |
AreaSGN
Creation of signatures and spectral statistics from training areas |
It creates the SGN spectral signature files of all the spectral bands of an image from some training areas.
|
| Unsupervised classification |
IsoMM
Unsupervised classification |
It performs an unsupervised image classification based on Duda and Hart's IsoData method:
|
| Hybrid (mixed) classification |
ClsMix
Hybrid (or mixed) classification of images |
It performs an Hybrid (mixed) classification of remote sensing images. The adjective hybrid (or mixed) is used because the classification method combines elements of a supervised classification (the training areas) with elements of an unsupervised classification (the results of the latter).
|
| Supervised classification |
ClasSup
Supervised image classification |
It does a supervised classification based on classical classifiers as: minimum Euclidean distance, minimum Manhattan distance and maximum likelihood.
|
| Number of nearest neighbors (k-NN) classifier |
ClaskNN
Number of nearest neighbors classifier |
performs a supervised classification of an image (monoband or multiband) using the kNNmethod. kNN is the acronym for k (which refers to a preset number of pixels from the pixels used to define the desired classes on the categorical map to be obtained) and NN (nearest neighbors). The method assumes that it is plausible that the pixels that are close to each other in the statistical space belong to the same informational class.
|
| Generate a confusion matrix |
MatConf
Generate a confusion matrix for evaluating thematic maps |
It creates a 'Confusion Matrix', a two dimensional table comparing the classified image data with reference to ground truth data. The output format may be a text file or a file in spreadsheet format (CSV).
|
| Selective filter |
FagoVal
Selective filtering of raster values |
It takes a raster and substitutes the cells (pixels) which have a value equal to a previously selected value (value to substitute) with the value of the majority of the cells surrounding that cell (mode) or the average of the neighboring values. The neighborhood is defined by the convolution window, which is square and has an odd number of pixels. The file to be processed is a raster in any format (byte, short integer, unsigned integer o real), compressed or uncompressed. The result of the process will be another raster in the same format.
|
Tools | Image processing |
Histogram |
Histo
Histogram of a raster |
It generates a histogram of frequencies of a raster in IMG format.
|
| Dilation of pixels in rasters |
Dilata
Dilation of pixels of a selected value in raster files |
It performs the image processing operation and mathematical morphology known as dilation, which takes a value and replicates it in the geometric immediate surroundings.
|
| Selection of a subset of raster cells |
RasSelec
Selection of a subset of raster cells |
It selects a subset of cells from a single-band or multiband raster, from the IMG format or by reading the file through the GDAL/OGR libraries.
|
| Rasters statistics |
EstRas
Statistical data of a raster or a raster series |
It calculates statistical data of raster images in which it is possible to choose between three options: the calculation of statistical data of a single raster (monoband or multiband), the calculation of an image with the result of the chosen statistical function in a raster series and the standardization of a raster (monoband or multiband)
|
| Images correlation |
CorrelIm
Images correlation |
It adjusts a regression line between the values of the first raster, which acts as an independent variable, and the second raster, which acts as a dependent variable. This adjustment gives rise to the corresponding correlation coefficient r (Spiegel 1991, 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill) and defines the slope and the independent term that characterize the correlation between the two variables.
|
| Spatial autocorrelation analysis (Moran) |
AutoCor
Spatial autocorrelation analysis (Moran) |
It allows quantifying the degree of spatial autocorrelation of a variable in a raster file by calculating an indicator, in this case the Moran's I(i) index.
|
Image transformation between color spaces (24 8, HSI) 8, HSI) |
RGBPal
Image transformation between color spaces |
It allows transformations between different color spaces. For example, it can transform a byte image with palette (8-bit color coding) into 3 separate byte images (R, G, and B bands 24-bit color coding). It can also convert 3-byte images representing the R, G, and B bands to an 8-bit (byte) image and an optimized palette, obtained from the analysis of the most frequent and unique colors present in the 3 original images.
|
| Indices of vegetation, snow, water, etc |
Indexs
Computing of indices of vegetation, snow, water, etc |
It allows to easily calculate vegetation indices and other indices of interest in remote sensing.
|
| Principal Component Analysis |
ACP
Principal Component Analysis |
It allows a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) on raster images (that are treated as variables), based on the variance - covariance matrix or correlation by calculating the corresponding eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
|
| Tasseled Cap transformation |
TassCap
Tasseled Cap transformation |
It allows obtaining new bands from a linear combination of the original.
|
| Optimizing the histogram (global, local) |
OptiIMG
Image enhancement by optimizing the histogram |
It improves the images by globally histogram optimization or locally optimizing the histogram using a window with a size defined by the user.
|
| Filter |
Filtres
Indiscriminate filtering of raster values |
It generates a raster as the result of the application of a specified convolution filter to an input raster. Each pixel in the input raster is substituted in the output raster by the result of the calculation defined according to the filter. This calculation uses all the pixels in a square window, defined by the user, centered on the original pixel and which has an odd number of pixels along each side.
|
| Selective filter |
FagoVal
Selective filtering of raster values |
It takes a raster and substitutes the cells (pixels) which have a value equal to a previously selected value (value to substitute) with the value of the majority of the cells surrounding that cell (mode) or the average of the neighboring values. The neighborhood is defined by the convolution window, which is square and has an odd number of pixels. The file to be processed is a raster in any format (byte, short integer, unsigned integer o real), compressed or uncompressed. The result of the process will be another raster in the same format.
|
| Generate a confusion matrix |
MatConf
Generate a confusion matrix for evaluating thematic maps |
It creates a 'Confusion Matrix', a two dimensional table comparing the classified image data with reference to ground truth data. The output format may be a text file or a file in spreadsheet format (CSV).
|
| Computing of SPI and SPEI drought indices |
SPI_SPEI
Computing of SPI and SPEI drought indices |
It allows to calculate the drought index SPI and SPEI.
|
| Compute the Terrestrial Connectivity Index |
ICT
Compute the Terrestrial Connectivity Index |
It generates a BAT/PS1 file that allows the calculation
of a raster layer that covers a certain study area, where each cell contains the Terrestrial Connectivity Index (TCI) for that cell center, or focal point, according to Pino formula, modified from that of Hanski.
|
Tools | Cartographic
generalization |
Raster |
Indiscriminate generalization |
Filtres
Indiscriminate filtering of raster values |
It generates a raster as the result of the application of a specified convolution filter to an input raster. Each pixel in the input raster is substituted in the output raster by the result of the calculation defined according to the filter. This calculation uses all the pixels in a square window, defined by the user, centered on the original pixel and which has an odd number of pixels along each side.
|
| Selective generalization |
FagoVal
Selective filtering of raster values |
It takes a raster and substitutes the cells (pixels) which have a value equal to a previously selected value (value to substitute) with the value of the majority of the cells surrounding that cell (mode) or the average of the neighboring values. The neighborhood is defined by the convolution window, which is square and has an odd number of pixels. The file to be processed is a raster in any format (byte, short integer, unsigned integer o real), compressed or uncompressed. The result of the process will be another raster in the same format.
|
Vector |
Line generalization |
GenVLin
Line generalization |
It generalizes the lines of a line layer (ARC or VEC of lines).
|
| Polygons boundary generalization |
GenVPol
Polygons boundary generalization |
It generalizes the boundaries (arcs) of a polygon layer.
|
| Polygons dropping |
MicroPol
Erase polygons and micropolygons of a polygon or categorical raster layer |
It allows removing micropolygons from a polygon file or a categorical raster.
|
Tools | Raster-vector
conversion |
Rasterization of points, lines and polygons |
TiraVec
Rasterize vector files |
It takes a vector point file, a line/arc file, a polygon or node file (whether structured or not) and rasterizes it using an existing or new raster.
|
| Vectorization of categorical rasters |
RasTop
Vectorization of categorical rasters |
It vectorizes one or several categorical raster files (land cover maps, geological maps, etc) to create a topologically structured polygon file.
|
| Vectorization of rasters to points |
IMGPNT
Creation or updating of PNT files from a monoband or multiband raster |
It allows to obtain a points file from a monoband or multiband raster file, so that the value of each cell in the raster will be saved in a field in the database table of the points file.
|
Tools | GPS |
GPS data capture in real time |
GPSMM
GPS data capture in real time |
It allows capturing data from GPS receivers and converting them into a line file that is represented in real time on cartography (orthophoto, topographic maps, etc).
|
| Import/Export from GPS to MiraMon |
GarminMM
Data interchange with a Garmin GPS |
It loads and downloads objects (points and lines) from the models of GPS of the GARMIN range to MiraMon through the computer's serial and USB ports.
|
| Import from GPX (GPS eXchange Format) to MiraMon |
GPXMM
Import and export between GPX and MiraMon format |
It allows to convert a GPX format file (GPS eXchange Format) into MiraMon structured vector format (PNT, ARC/NOD) and viceversa.
|

MSAs are applications that can be run from the system command line or from the Windows graphical interface. The functionalities are exactly the same; the only difference is in the way the parameters are prepared. The following options for using MSA are available:
1. Execution of the MSA from MiraMon
The MSA graphic interface can be accessed from the MiraMon menus (for example, most of the import/export functions are in the "File" menu). With this interface it is possible to enter the file names (browsing the directory tree with the standard browser), select different options with buttons, blinds, etc, and access the help if necessary using the button  . When the parameters are correct, it is possible to press the button . When the parameters are correct, it is possible to press the button  , so the application is launched and the interface closes. The process information that is executed is the same as if it had been executed from the command line. , so the application is launched and the interface closes. The process information that is executed is the same as if it had been executed from the command line.
Each interface of the MSA "remembers" the last parameters used, even if the program is closed (this is because the parameters are saved in the *.par file, where * is the name of the application that has been used). This works even in network configurations.
Those MSA (or groups of MSA) that use Windows interface and that are present in the MiraMon menus are marked with a (*). This informs the user that, on the one hand, they are functionalities implemented as external applications (and that, if desired, they can be part of a metaprogram or BAT process), and on the other hand, the inputs and outputs of these applications are totally independent of the files displayed at that time with MiraMon. The files generated by any application are offered to be opened in the MiraMon session from which the corresponding application has been called. This functionality is configurable from the ObrirResultatMSAaMiraMon= key of the [MSA] section of the MiraMon.par. If this new functionality is activated (activated by default), as the Director asks which session the user wants to open the result (by preselecting the session that originated the result), the user can also cancel, thereby maintaining the original philosophy of the program of not wasting time waiting for the results if they are not desired. For example, if a clipping of a MiraMon layer is executed it is possible to select in which MiraMon session visualize the results once the clipping process is finished.
 2. Execution of the MSA from the command line (C:\>)
MSA can also be run from the command line of the system, which will show the execution syntax. If the user writes the name of the application followed by a blank space and the question mark the user will get more extensive help. For example:
CreaTop (access to the syntax section included in the MSA help)
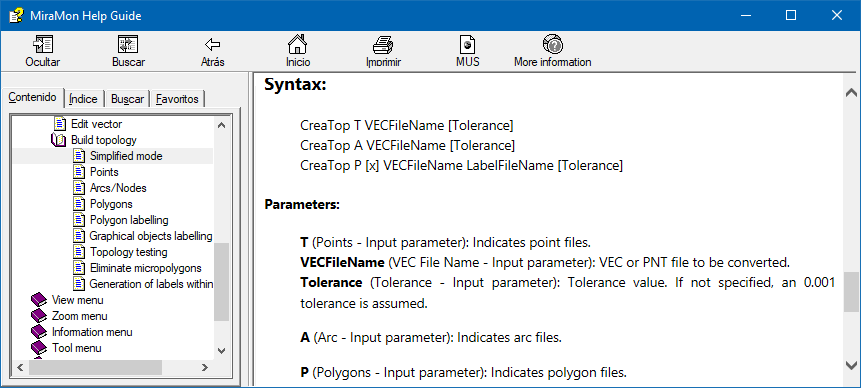 CreaTop ?
CreaTop ? (access full MSA help)
When the desired parameters are known, write the complete command line:
CreaTop T
C:\CARTO\PUNTS\POUS
In the previous example it is assumed that the MiraMon directory is included in the path (see the operating system manual for more details). Otherwise, add the address to the name of the MSA:
F:\SERVER\MIRAMON\CreaTop T
C:\CARTO\PUNTS\POUS
3. Execution of the Windows Interface of the MSA from the Command Line (C:\>)
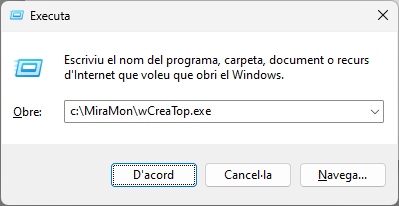
When working with Windows, the graphical interface of any MSA can be run simply by entering the name of the application preceded by a "W" in Start | Run or from an operating system window:
It is even possible, on the command line, to make any application start in one of the three available language versions, by adding the parameter /IDIOMA=### where ### is CAT, SPA or ENG. For example, it is possible to invoke "wCreaTop /Idioma=CAT" and the program will start in Spanish.
C:\MiraMon>wCreaTop (access to the syntax section included in the MSA help)
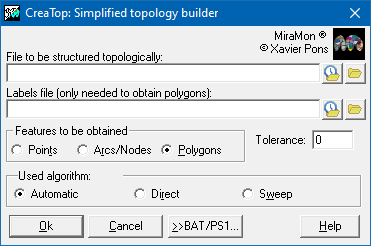 C:\MiraMon>wCreaTop /IDIOMA=CAT
C:\MiraMon>wCreaTop /IDIOMA=CAT (access full MSA help)
If the default language on a computer has to be a specific one, simply copy *.### *.stb located in the MiraMon directory, again replacing ### with cat, spa or eng (it is not case sensitive).
If the name of the application has 8 characters, the last one must be cut. For example "wCorrGeom" to execute the graphical interface of "CorrGeom". As explained above, if the MiraMon directory is not in the path, the user must add the complete directory before the name of the application:
C:\MIRAMON\wCreaTop
Many of the users who prefer to work from the command line can use this method to introduce, in an easier way, the necessary parameters for each application. The advantage of launching the graphic interfaces of the MSA from the command line is that the user does not have to look for the functionality in the MiraMon menu, so it is not essential to have MiraMon open.
With the aim of offering (and improving) the functionality of the system by repeating the last command line using the "up arrow" of the keyboard, each Windows interface of the MSA "remembers" the parameters of the last execution, even after the computer is turned off (this is due to the fact that the parameters are saved in a *.par file, where * is the program that has been executed).
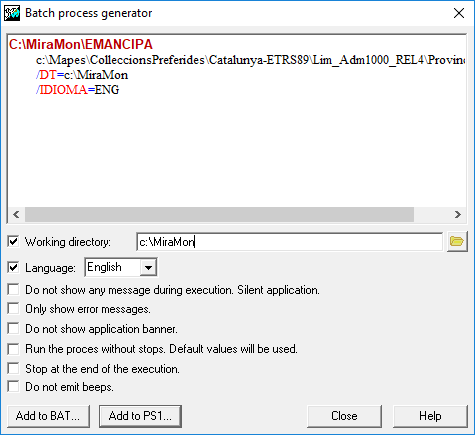
4. Write BAT files from the Windows MSA interface
Some users write metaprograms using MSA, both from BAT files and from programs written in C, Pascal, etc. To facilitate this task, MiraMon provides a batch process generator accessible from the Windows MSA interface with the button  . .
The batch process generator visualizes the current command line, built from the Windows interface in a clear and differentiated way. It provides a method of manipulating the command line to modify general syntax parameters such as the Working Directory.
By clicking on the text with the right mouse button the user can copy the line to the clipboard and attach it to other editors. The user can also copy the plain text on a command prompt to execute the program immediately.
Through the "Add to BAT" button, the current command line is written to any BAT file. Once introduced in the file, it is possible to open it with an editor and replace the names of the files with variables and environment parameters (%1,%2, etc, for arguments and %VAR% for environment variables, etc). In this way it is possible to build metaprograms in a simple, fast and reliable way.
The last created BAT file is always "remembered" by the other MSA because its name is written in the "LastBatName" field of the [Batch] section of the MiraMon.par file.
Some consideration
MSA Windows Interfaces shortcut personalization
Users of the MSA and its graphic interface can create a shortcut icon to any of them on the desktop.

When editing the properties of the shortcut it is possible to configure "hotkeys" to run the application (for example Control + Alt + T for TIFIMG). See the Windows manual for more details on shortcut properties.
Fine-tuned execution of the MSA
In addition to the parameters of each MiraMon Support Application, any of them support the following parameters. These allow a fine control execution of the application, especially when they are executed from BATs or from other programs that user can write. The parameters can be indicated in any order and position on the command line.
a) GENERAL SYNTAX PARAMETERS
Without any parameter: Shows the syntax of the application.
? (single parameter): Shows the complete help of the application.
/DT: Specifies the current working directory from where the application launches (for more information see Command line parameters). When the specified directory contains a MiraMon configuration file (MiraMon.par) or geodesy tables, these prevail over the configuration file of the MiraMon directory. The path of all the files specified in the command lines of the console application are relative to this directory.
/MUT: The application runs without saying anything (mute), even in case of error. The screen is not cleared either.
/SIL: This setting prevents apps from emitting audible alerts (like /MUT, but the new setting does display screen messages).
/BAN: The application does not show the presentation screen. The screen is not cleared either.
/ERR: The application does not show the presentation screen. The screen is not cleared either.
/SAC: The application never stops before a question, unless the introduction of data by the user becomes necessary, which is very rare in the MSA. In these cases, remember that it is possible to indicate to the Operating System the parameters that would be introduced through a redirector. All "Press any key" requests are bypassed using /SAC.
/STP: The application stops (STOP) at the end of the program waiting for any key to be pressed. This is useful when calling the program from a Windows interface (as MiraMon does), or from an "Execute" Program Manager or the Windows "Start" menu.
Examples:
VECPNT 2 C:\PROJECT\POINTS
C:\PROJECT\POINTS /MUT 5
VECPNT /SAC /ERR 2
C:\PROJECT\POINTS C:\PROJECT\POINTS 5
Some applications also share other syntax parameters. For more information, see General Syntax Aspects in MiraMon Support Applications.
b) REDIRECTORS
The MSA supports the standard DOS and UNIX redirectors "<" and ">".
c) ERROR LEVELS
The a MSA return the following error levels to the Operating System:
0: The process has finished properly.
1: An error has occurred, which is explained in the messages that are displayed on the screen before the end of the program.
2: The help of the program has been requested or the syntax was incorrect.
Error levels are useful for controlling the flow of metaprograms built with BATCH processes or through calls from other applications.
d) COMMAND LINES OF MORE THAN 128 CHARACTERS
The Operating System does not support command lines of more than 128 characters. In some cases, especially when the user has the data in "very long" directories, this limit can be exceeded. For example, imagine trying to write the following statement on the command line of the system:
LinArc 3
C:\USERS\DATA\MAPS\HOLLAND\CHANNELS 0 "Channel navigability level" NIV_NAVEGA
The user will notice that this command line can not be written because it is too long. In some configurations of the system it may be possible to execute it if the user writes the command in a BAT file, but it is possible to not obtain a correct result if the user extends the line beyond 260 characters.
When this happens it is possible to dodge the problem in one of two ways:
1: Use the SUBST command of the operating system. For example, if the user types:
SUBST Z:
C:\USERS\DATA\MAPS
The user can write the previous syntax:
LinArc 3 Z:CHANNELS Z:CHANNELS 0
"Channel navigability level"
NIV_NAVEGA
and have it run without problems. See the Operating System manual for more information about the SUBST command.
2: Write the parameters inside a text file, a parameter in each line, and execute the application followed by the name of the file, preceded by the symbol '@'. For example, if the user edits a PARAM.TXT file with the following content:
3
C:\USERS\DATA\MAPS\HOLLAND\CHANNELS
C:\USERS\DATA\MAPS\HOLLAND\CHANNELS
0
"Channel navigability level"
NIV_NAVEGA
The user can write the previous syntax:

|