-
 InsolDia: Computation of the solar radiation in a single day or an instant
InsolDia: Computation of the solar radiation in a single day or an instant
Direct access to online help: InsolDia
Access the application from the menu: "Tools | Terrain interpolation and analysis | Compute solar radiation"
Presentation
This application calculates the incident solar radiation (in units of energy, not power) at each point on the ground during a given day of the year. It also allows to make the calculation in a time interval throughout the day (not all day) and instantaneously at a specific moment of the day. To make these calculations, this application uses a Digital Elevation Model (DEM). In addition to solar irradiance, atmospheric transmittance, angles of incidence, projected shadows, distance from the Earth to the Sun and other parameters specified later, the application takes into account the position of the Sun in user-defined time intervals (hourly, for example, except in the instant case, where the interval is not used).
The diffuse radiation is estimated as a percentage of the direct radiation in a similar way to that proposed with the equation of Page (1986), adjusted by Baldasano et al. with data from Catalonia in 1994; the percentage can be specified as a constant value (via the percent_difus parameter of the command line, applying a simplified model called Constant Atmospheric Conditions, CAC) or by providing a raster that will indicate the percentage at each point in the terrain (applying a more sophisticated model, called InsolMets, via the /PERC_DIF_VS_DIRECT= modifier, and then percent_difus is ignored). The direct radiation from which the diffuse radiation is calculated corresponds to the direct radiation on a clear day, which prevents that if the direct radiation is zero or very small due to very thick clouds, the diffuse radiation ends up being practically non-existent, which would not be realistic; for this purpose, the parameter tau_0_clear_day is used (guide values are indicated later). CAC and InsolMets also differ by the introduction of parameters allowing to consider the Cloud Fractional Cover and/or the Extinction coefficient, tau_0, at each point of the terrain (from raster digital models), as will be shown in the dialog box and explained in the syntax section.
It is necessary to provide the solar exoatmospheric spectral irradiance for the desired range of wavelengths, in W/(m2·µm), [or the solar exoatmospheric irradiance, in W/m2], extinction coefficient tau_0 (τ0, or optical depth) (exponent to compute transmittance) and the shadows files in predefined intervals (e.g., one hour) (it is suggested to create a BAT or PS1 to write them automatically from the Ombra application). If the calculation for the whole solar spectrum is desired, the suggested value for the solar exoatmospheric irradiance is 1366 W/m2 (ISO 21348:2007), and the value of 0.288 as tau_0 (average clear forest atmosphere, Rothermel et al. 1986).
The solar position is calculated for the center of the DEM. The result of the application is a file in 10 kJ/(m2·day·µm) in the case of providing spectral irradiances, or in 10 kJ/(m2·day) in the case of providing irradiances, both for calculations throughout the whole day, and in time intervals specified by the user (in this case the units are documented by "partial day"). In the case of instantaneous calculations (actually the second of the indicated time is taken), the units become J/(m2·s·µm) and J/(m 2·s), respectively for the spectral and non-spectral cases. To specify that the irradiance data provided is spectral, the optional modifier /IRRAD_ESPEC=1 can be used, although it is not necessary as it is the default criterion; otherwise, it is necessary to indicate /IRRAD_ESPEC=0. The file is, by default, stored in a 2-byte/cell integer raster; for a real 4-byte/cell file, the optional modifier /DadesRad=Real_10kJ must be used (which will actually be real joules in case of instant calculation). During the calculation, the DEM, the illumination matrix and the temporary radiation calculation matrix are loaded into memory.
Note 1: Typically, when the given exoatmospheric irradiance is the solar constant [which includes the entire solar electromagnetic spectrum] it is convenient to indicate to be documented as 10 kJ/(m2·day) [or in J/(m2·s) in instant calculations] using the /IRRAD_ESPEC=0 modifier, while when the user wants to calculate radiation in a particular spectral region, such as red, the exoatmospheric irradiance provided is usually spectral [per unit wavelength] and the units should be documented as 10 kJ/(m2·day·µm) [or J/(m2·s·µm) in instant calculations], for which there is no need to indicate anything special, or /IRRAD_ESPEC=1 can be specified.
Note 2: If at latitudes close to the poles the calculation is requested on a date when the Sun does not rise at any time of the day, zero radiation values are generated, except in areas where there is no data in the DEM, in which a NoData is also written.
Note 3: If the units of the DEM are not the same as the planimetric ones, the application also does the calculation correctly, or warns if it does not know how to perform the conversion.
Note 4: To convert the units obtained from 10 kJ/(m2·day) to kWh/(m2·day) it is necessary to divide the values by 360.
Papers that show and discuss the used algorithm:

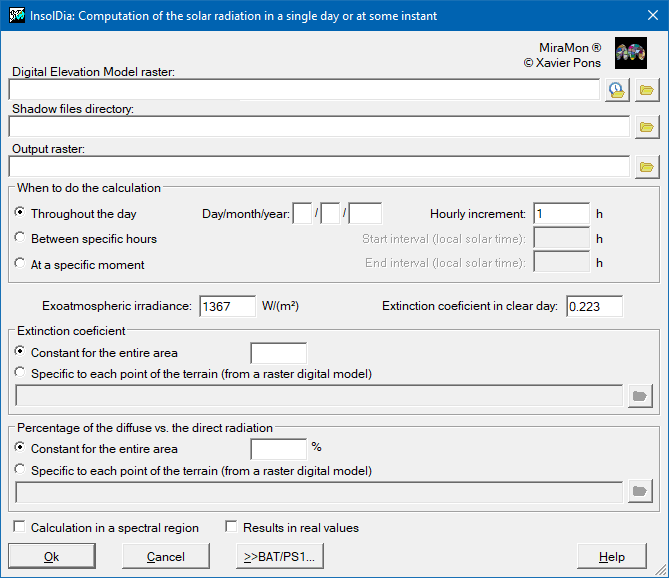
Dialog box of the application

Graphic examples
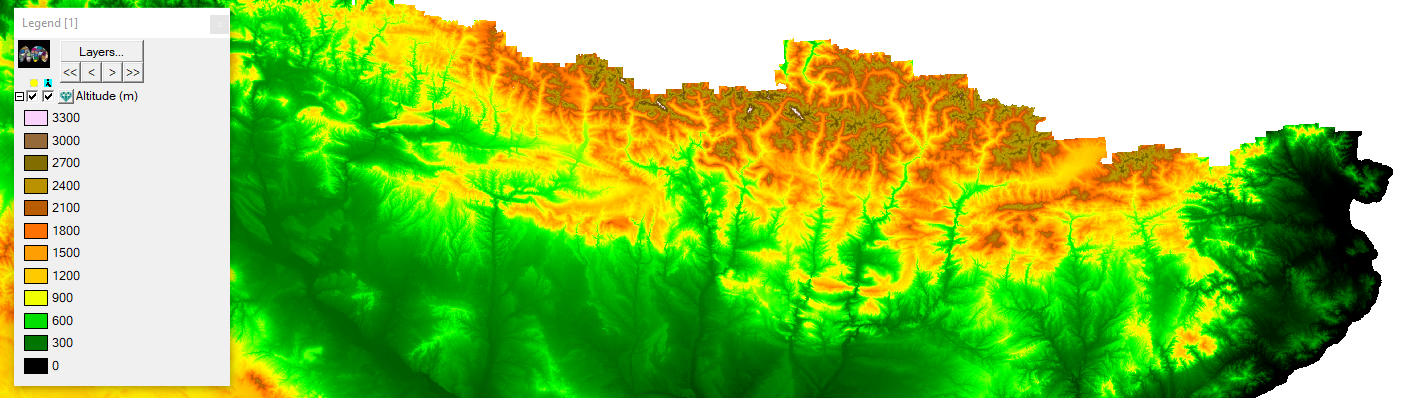
|
| Digital Elevation Model of an area of the Iberian Peninsula and calculation of solar radiation on December 15, 2023 with the default parameters. |

Syntax
Syntax:
- InsolDia DEM shadow_directory output_file day month year exoatmospheric_irradiance tau_0 hourly_increase tau_0_clear_day percent_diffuse [/INSTANT] [/INICI] [/FINAL] [/TAU_0] [/PERC_DIF_VS_DIRECT] [/IRRAD_ESPEC] [/DadesRad] [/CFC] [/TAU_0_CelClar]
Parameters:
- DEM
(Digital elevation model -
Input parameter): Digital elevation model in IMG raster format.
- shadow_directory
(Shadow directory -
Input parameter): Directory where the different models derived from the DEM generated with Ombra application have been saved. It is necessary to have a series of models that contain the range of possible azimuths that will occur during the chosen day. Within this range, representative ones will be generated (e.g., every 10 degrees) and must have their corresponding azimuth by name (0.img, 10.img..., ...100.img, 110.img, 120.img...). The application automatically determines (from the file names) the angular interval between available shadow layers (10 degrees in the example above). The minimum admissible interval is 1 degree (files ... 111.img, 112.img, 113.img...), but with intervals of the order of 10 degrees sufficiently precise results are usually obtained. If working in an area where the 360.img file may be needed (for example in areas near the North Pole at the end of June), it will have to be created (or created as a duplicate of the 0.img file).
- output_file
(Output file -
Output parameter): IMG raster result of solar radiation calculation.
- day
(Day -
Input parameter): Day for which the solar radiation calculation is carried out.
- month
(Month -
Input parameter): Month for which the solar radiation calculation is carried out.
- year
(Year -
Input parameter): Year for which the solar radiation calculation is carried out.
- exoatmospheric_irradiance
(Exoatmospheric irradiance -
Input parameter): Estimated value of solar irradiance that reaches the outside of the Earth's atmosphere, in W/m2 (or in W/(m2·µm) in calculations in specific spectral regions); 1366 is suggested in the non-spectral case.
- tau_0
(Extinction coefficient -
Input parameter): Extinction coefficient; 0.288 is suggested. This is used when running the CAC model. If the user runs the program with the /TAU_0= modifier, tau_0 is ignored since the calculation is based on the raster data indicated with this modifier at each point in the territory; it is suggested, for neatness, to indicate a value of -1 to tau_0 in this case.
- hourly_increase
(Hourly increase -
Input parameter): Increase, in hourly units, that is applied to the new solar position from the starting position and successively, to determine a new instantaneous calculation of potential radiation that represents the defined interval on average. 1 is suggested, but it can be used, for example 0.5 for calculations every 30', or 2 for calculations every 2 hours (less accurate, but faster). If the user runs the application with the /INSTANT= modifier, the hourly increment is ignored since the calculation is only done at the time requested; it is suggested, for neatness, to specify a value of -1 in the increment_horari in this case.
- tau_0_clear_day
(Extinction coefficient in a clear day -
Input parameter): It allows a more reasonable diffuse radiation calculation. 0.223 can be used for an exceptionally clear atmosphere, or 0.288 for an average forest clear atmosphere (Rothermel et al. 1986).
- percent_diffuse
(Percentage of diffuse vs direct radiation -
Input parameter): Percentage of diffuse radiation (calculated with tau_0_clear_day) with respect to direct radiation. Typically a value of 20 for 20 % can be applied. This is used when running the CAC model. If the user runs the program with the /PERC_DIF_VS_DIRECT= modifier, percent_difus is ignored since the calculation is based on the raster data indicated with this modifier at each point in the territory; it is suggested, for neatness, to specify a value of -1 to percent_difus in this case.
Modifiers:
/INSTANT=
(Instantaneous calculation)
Restricts the calculation, which by default is daily accumulated, to only an instantaneous calculation (for 1"). The value must be indicated as local solar time. (Input parameter) /INICI=
(Start interval)
Allow defining the beginning of a time interval (within the specified day) for the accumulated calculation of solar radiation. Values are reported as local solar time. In this case the units are documented by "partial day". (Input parameter) /FINAL=
(End interval)
Allow defining the end of a time interval (within the specified day) for the accumulated calculation of solar radiation. Values are reported as local solar time. In this case the units are documented by "partial day". (Input parameter) /TAU_0=
(TAU_0)
It is allowed, through the optional parameter /TAU_0=, that TAU_0 be a specific value for each cell of the MDE (for example from atmospheric remote sensing data). This is used when running the InsolMets model. In this case, /TAU_0= will indicate where is the raster that contains the values of TAU_0 in each cell; for example /TAU_0=c:\RadSolar\TAU_0_10-maig.img. This raster contains 4-byte real values and will have the same Horizontal Reference System (HRS) and dimensions as the MDE; CanviPrj and/or AdapRas can be used if needed. When the /TAU_0= parameter is specified the application ignores the eighth parameter of the command line (which is a general TAU_0 value for the entire raster); in this case it is suggested to indicate, for neatness, a value of -1 in the eighth parameter. (Input parameter) /PERC_DIF_VS_DIRECT=
(PERC_DIF_VS_DIRECT)
It is allowed, through this optional parameter, that the percentage of diffuse radiation in relation to direct radiation be a specific value for each cell of the MDE (for example by interpolating data from solar radiation ground stations). This is used when running the InsolMets model. In this case, /PERC_DIF_VS_DIRECT= will indicate where is the raster that contains the percentage values in each cell; for example /PERC_DIF_VS_DIRECT=c:\RadSolar\Perc_difusa_vs_directa.img. This raster contains 4-byte real values and will have the same SRH and dimensions as the MDE; CanviPrj and/or AdapRas can be used if needed. When the /PERC_DIF_VS_DIRECT= parameter is specified, the application ignores the eleventh parameter of the command line (which is a general percentage value for the entire raster); in this case it is suggested to indicate, for neatness, a value of -1 in the eleventh parameter. Raster values are expressed as a percentage. (Input parameter) /IRRAD_ESPEC
(IRRAD_ESPEC)
It is allowed to indicate whether the units to be documented are irradiance (0 must be indicated, for "false"), typical when the exoatmospheric irradiance provided is the solar constant (in this case 10 kJ/(m2·day) will be documented for example), or spectral irradiance [per unit wavelength] (1 must be specified, for "true"), typical when to calculate radiation in a spectral region, such as red, and the exoatmospheric irradiance provided is spectral [per unit wavelength] (in this case for example 10 kJ/(m2·day·µm) will be documented); it should be noted that the indicated units are only examples and may change depending on whether the application works in instant mode, etc. The default value is 1, which corresponds to application versions prior to September 2023. (Input parameter) /DadesRad=
(DadesRad)
It is allowed to indicate Int_10kJ whether the desired output format is 2-byte signed rounded integers of "10 kJ/(m2·day·µm)" (read "tens of kilojoules...") or the units that apply according to the execution mode; Int_10kJ is the default mode and equal to application versions before September 2023. If the results are desired in real 4-byte real numbers it must be indicated Real_10kJ. (Input parameter) /CFC=
(CFC)
It allows to indicate, through a raster, the fraction of cloud cover (Cloud Fractional Cover), assigning a specific value for each cell of the DEM (e.g., from atmospheric remote sensing data of CFC). In this case, /CFC= will indicate where the raster containing the CFC values in each cell is; e.g., /CFC=c:\SolarRad\CFC_10-may.img. This raster must contain real 4-byte values and have the same HRS and dimensions as the DEM; it is possible to use CanviPrj and/or AdapRas if necessary. The raster values are expressed as per unit; a completely cloud-covered atmosphere in a pixel has a value of 1, and a completely clear atmosphere has a value of 0. This modifier must be supplied together with the /TAU_0_CelClar= modifier. This is used when running the InsolMets model. (Input parameter) /TAU_0_CelClar=
(TAU_0_CelClar)
It allows to indicate the extinction coefficient of solar radiation in the clear sky fraction. If this modifier is provided, the coefficient tau_0 parameter (or the /TAU_0= modifier as a raster) is interpreted as the extinction coefficient of solar radiation in the cloudy sky fraction. It is suggested to enter a value similar or equal to that provided in the tau_0_dia_clar parameter. This modifier must be provided together with the /CFC= modifier. This is used when running the InsolMets model. (Input parameter)